Network-Controlled Small Gap (NCSG) in 5G NR MR-DC
Network-Controlled Small Gap (NCSG) is a sophisticated measurement gap mechanism introduced to mitigate the throughput degradation inherent in legacy per-UE measurement gap configurations. While standard measurement gaps (MG) are characterized by a complete suspension of transmission and reception across all serving cells, NCSG leverages advanced UE receiver architectures to allow concurrent data processing on a subset of carriers while performing inter-frequency or inter-RAT measurements.
1. Technical Context & Scope
The NCSG framework primarily resides within the RAN2 (protocol signaling) and RAN4 (RF/RRM requirements) domains. It is specifically targeted at Multi-Radio Dual Connectivity (MR-DC) architectures, including:
- EN-DC (E-UTRA-NR Dual Connectivity)
- NR-DC (NR-NR Dual Connectivity)
- NGEN-DC and NE-DC
In the 3GPP protocol stack, NCSG is configured via Radio Resource Control (RRC) signaling and managed at the Media Access Control (MAC) layer for timing alignment. It operates under the requirements specified in TS 38.133 (NR RRM) and TS 36.133 (E-UTRA RRM).
2. Functional Objective: Mitigating Gap Overhead
In standard per-UE gap configurations, the UE hardware is assumed to be incapable of simultaneous measurement and data transfer. This results in a strict "all or nothing" approach where a 6ms gap (Pattern 0) periodically blanks out 15-18% of the available airtime in both DL and UL across all Frequency Ranges (FR).
The MR-DC Constraint
In MR-DC, a UE may have independent RF chains for FR1 and FR2 or different bands within FR1. Applying a per-UE gap across all carriers when only one RF chain is needed for measurement is architecturally inefficient. The objective of NCSG is to provide a "Small Gap" that:
- Provides a Visible Period (VP) for the UE to tune to a target frequency.
- Maintains non-interrupted data transfer on carriers that do not share RF components with the target frequency.
- Synchronizes these gaps through network control via the Master Node (MN) or Secondary Node (SN).
3. NCSG Architecture and Parameters
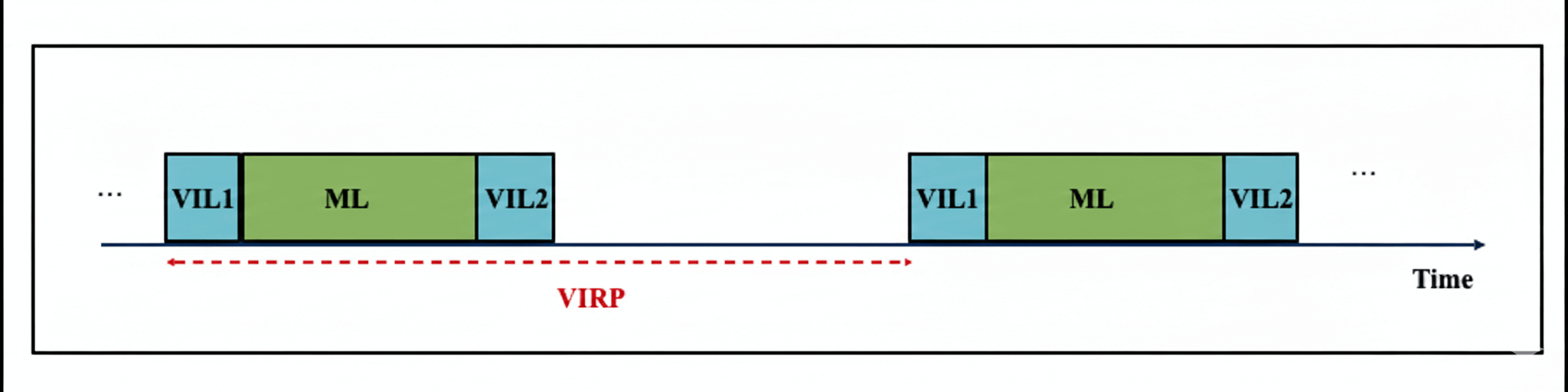
NCSG is defined by three primary timing components that diverge from the traditional MGL (Measurement Gap Length) and MGRP (Measurement Gap Repetition Period) model:
- Visible Period (VP): The actual duration where the UE performs the measurement.
- NCSG Sequence Length (NCSL): The total duration of the NCSG event, including switching times.
- : The small gap duration (typically shorter than standard MGL).
UE Signaling and Configuration
The UE initiates a request for NCSG by indicating its capability in the UE-NR-Capability or UE-MRDC-Capability IEs. The network responds with a configuration in MeasGapConfig using the ncsgInd (NCSG Indicator).
MeasGapConfig ::= SEQUENCE {
gapFR1 GapConfig OPTIONAL, -- Need M
gapFR2 GapConfig OPTIONAL, -- Need M
gapUE GapConfig OPTIONAL, -- Need M
...
}
GapConfig ::= SEQUENCE {
gapOffset INTEGER (0..159),
mgl ENUMERATED {ms1dot5, ms3, ms3dot5, ms4, ms5dot5, ms6},
mgrp ENUMERATED {ms20, ms40, ms80, ms160},
mgta ENUMERATED {ms0, ms0dot25, ms0dot5},
...,
[[
ncsgInd-r16 ENUMERATED {supported} OPTIONAL -- Rel-16 NCSG
]]
}
Interrupted Slots in NR Standalone (Single Carrier/CA)
Per-UE Patterns #0-11 or per-FR FR1 NCSG (VIL = 1 ms)
| NR SCS (kHz) | Interrupted Slots (MGTA = 0 ms) |
|---|---|
| 15 | 1 |
| 30 | 2 |
| 60 | 4 |
| 120 | 8 |
[!NOTE] NR SCS of 120 kHz is only applicable to per-UE NCSG.
Per-UE Patterns #12-23 or per-FR FR2 NCSG (VIL = 0.75 ms)
| NR SCS (kHz) | Interrupted Slots (MGTA = 0 ms) | Interrupted Slots (MGTA = 0.75 ms) |
|---|---|---|
| 60 | 3 | 3 |
| 120 | 6 | 6 |
In Rel-17, NCSG was further refined to support MUSIM (Multi-Universal Subscriber Identity Module) scenarios, where small gaps are used for monitoring paging or reading SIBs on a secondary network without dropping the primary connection.
NCSG Configurations supported
NCSG patterns are defined in TS 38.133 Table 9.1.2-1. Unlike standard gaps, NCSG requires precise handling of mgta (Measurement Gap Timing Advance) to prevent collisions with Uplink transmissions.
| NCSG Pattern Id | Measurement Length during which there is no gap (ML, ms) | Visible interruption Repetition Period (VIRP, ms) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 40 |
| 1 | 5 | 80 |
| 2 | 2 | 40 |
| 3 | 2 | 80 |
| 4 | 5 | 20 |
| 5 | 5 | 160 |
| 6 | 3 | 20 |
| 7 | 3 | 40 |
| 8 | 3 | 80 |
| 9 | 3 | 160 |
| 10 | 2 | 20 |
| 11 | 2 | 160 |
| 12 | 5 | 20 |
| 13 | 5 | 40 |
| 14 | 5 | 80 |
| 15 | 5 | 160 |
| 16 | 3 | 20 |
| 17 | 3 | 40 |
| 18 | 3 | 80 |
| 19 | 3 | 160 |
| 20 | 1 | 20 |
| 21 | 1 | 40 |
| 22 | 1 | 80 |
| 23 | 1 | 160 |
4. Implementation & Interoperability Considerations
RF Front-End Constraints
The feasibility of NCSG is heavily dependent on the UE's RF Front-End (RFFE) architecture. If the UE uses a shared LNA (Low Noise Amplifier) or localized oscillator across multiple bands, a "small gap" may still cause leakage or phase noise issues on the non-measuring carrier. 3GPP specifications define strictly defined interruption requirements for these scenarios.
Rel-15 vs. Rel-16/17 Backwards Compatibility
- Rel-15: Primarily supported per-UE gaps. NCSG was a boutique feature with limited deployment.
- Rel-16: Introduced per-FR gaps, which reduced the need for NCSG in some dual-FR scenarios but increased the complexity of gap coordination.
- Rel-17: Positioned NCSG as a core requirement for efficient MUSIM and RedCap (Reduced Capability) device operation.
Race Conditions
A critical implementation challenge is the alignment of the NCSG pattern when a handover occurs. The target cell must be informed of the ongoing NCSG pattern via the HandoverPreparationInformation message to avoid scheduling the UE during the configured mgta window.
NCSG represents a shift from static, destructive measurement gaps to a more granular, network-controlled approach. By limiting the "visible" interruption to specific periods and carriers:
- Spectral Efficiency is preserved in high-bandwidth MR-DC links.
- UE Power Consumption is optimized by avoiding full-stack resumption after a full gap.
- Mobility Reliability is maintained through deterministic measurement windows that the network can schedule around.
You must ensure that RRM algorithms correctly account for the shorter VP in NCSG when calculating measurement accuracy requirements (e.g., for RSRP).
Further Reading
WirelessBrew Team
Technical expert at WirelessBrew, specializing in 5G NR, LTE, and wireless system optimization. Committed to providing accurate, 3GPP-compliant engineering tools.
Up Next
More 5g nr Articles →