Difference between BLER for Radio Link Management and BLER in Data throughput
Difference between BLER for Radio Link Management and BLER in Data throughput
Difference between BLER for Radio Link Management and BLER in Data throughput
In 5G NR, Block Error Rate (BLER) is a critical performance metric used in two distinct contexts: Radio Link Management (RLM) and Data Throughput. While both use the same fundamental concept of measuring block errors, they differ significantly in their purpose, measurement methodology, and impact on network performance.
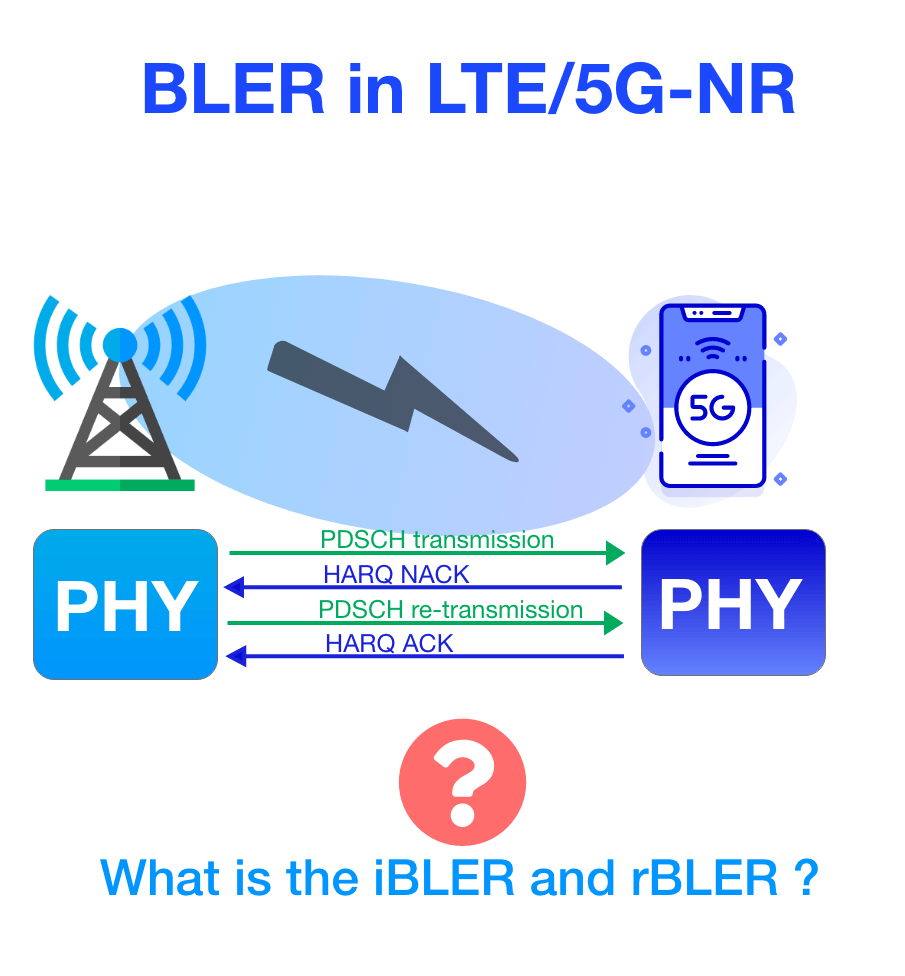
What is BLER?
Block Error Rate (BLER) is defined as the ratio of the number of incorrectly received transport blocks to the total number of transmitted transport blocks over a specific time period.
BLER = Number of Erroneous Blocks / Total Number of Transmitted Blocks
BLER for Radio Link Management (RLM)
Purpose
RLM BLER is used to monitor the quality of the radio link and determine when to perform handover or cell reselection. It helps the UE decide whether to stay connected to the current cell or move to a better one.
Measurement Methodology
- Measurement Object: RLM BLER is measured over a rolling window of 10 consecutive subframes.
- Trigger: The RLM BLER is calculated based on the CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) of the received transport blocks.
- Thresholds: The network configures two thresholds:
- RLM BLER1 (In-sync threshold): Typically set at 10% (0.1).
- RLM BLER2 (Out-of-sync threshold): Typically set at 2% (0.02).
- Behavior:
- If the measured BLER exceeds BLER1, the UE is considered out-of-sync with the cell.
- If the measured BLER drops below BLER2, the UE is considered in-sync with the cell.
Impact
- High RLM BLER: Indicates poor radio conditions, triggering handover or cell reselection to a better cell.
- Low RLM BLER: Indicates good radio conditions, allowing the UE to maintain connection to the current cell.
BLER in Data Throughput
Purpose
Data Throughput BLER is used to measure the efficiency of data transmission and determine the modulation and coding scheme (MCS) to use for future transmissions.
Measurement Methodology
- Measurement Object: Data Throughput BLER is measured over a rolling window of 100 ms (10 consecutive scheduling occasions).
- Trigger: The BLER is calculated based on the CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) of the received transport blocks.
- Thresholds: The network configures thresholds based on the MCS index being used.
- Behavior:
- The UE reports the actual BLER achieved for each MCS index.
- The network uses this information to select the optimal MCS for future transmissions that maximizes throughput while maintaining acceptable error rates.
Impact
- High Data BLER: Indicates that the current MCS is too aggressive, prompting the network to switch to a lower-order MCS (e.g., from 256-QAM to 64-QAM) to reduce errors.
- Low Data BLER: Indicates that the current MCS is appropriate, allowing the network to maintain or potentially increase the MCS for higher throughput.
Key Differences Summarized
| Feature | RLM BLER | Data Throughput BLER |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Monitor radio link quality for mobility decisions | Measure data transmission efficiency for MCS selection |
| Measurement Window | 10 consecutive subframes | 100 ms (10 scheduling occasions) |
| Trigger | CRC of transport blocks | CRC of transport blocks |
| Thresholds | Fixed (e.g., 10% and 2%) | Configurable based on MCS |
| Behavior | Triggers handover/cell reselection | Triggers MCS adaptation |
| Impact | Mobility decisions | Throughput optimization |
Practical Example
Scenario: A UE is connected to a 5G NR cell and is experiencing varying radio conditions.
RLM BLER Behavior
- Good Conditions: RLM BLER = 1% (below 2% threshold) → UE stays connected to current cell.
- Poor Conditions: RLM BLER = 15% (above 10% threshold) → UE triggers handover to a better cell.
Data Throughput BLER Behavior
- Current MCS = 256-QAM: Data BLER = 8% (acceptable for this MCS) → Network continues using 256-QAM.
- Current MCS = 256-QAM: Data BLER = 25% (too high for this MCS) → Network switches to 64-QAM to reduce errors.
Conclusion
While both RLM BLER and Data Throughput BLER measure block errors, they serve fundamentally different purposes in 5G NR. RLM BLER focuses on mobility decisions, ensuring the UE maintains a stable connection to the network, while Data Throughput BLER focuses on throughput optimization, enabling the network to adapt transmission parameters for maximum data rates. Understanding this distinction is crucial for comprehending how 5G NR manages radio resources and optimizes performance in diverse conditions.
Further Reading
WirelessBrew Team
Technical expert at WirelessBrew, specializing in 5G NR, LTE, and wireless system optimization. Committed to providing accurate, 3GPP-compliant engineering tools.
Up Next
More 5g nr Articles →