Measurement report Event A5 in 5G NR
Event A5 (SpCell becomes worse than threshold1 and neighbour becomes better than threshold2)
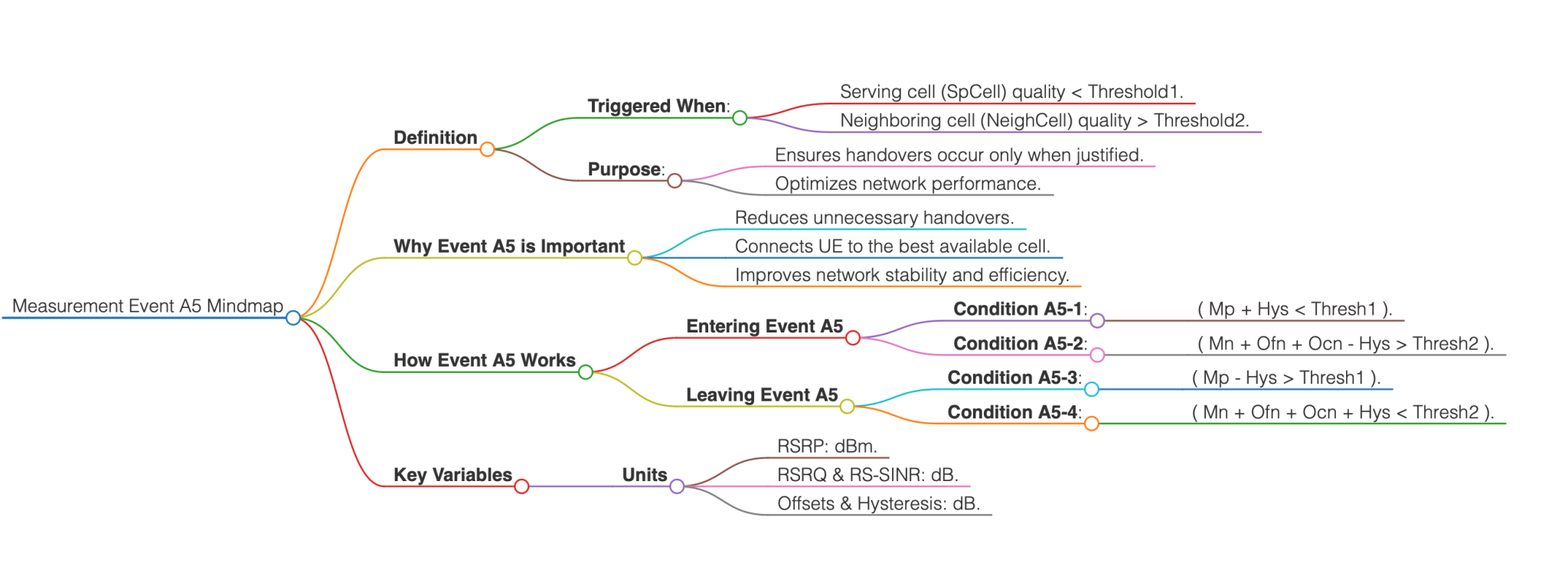
Measurement Event A5 is a critical event in 5G NR, used by UE to ensure optimal handovers between cells. Measurement Event A5 is triggered when:
- The serving cell (SpCell) signal quality becomes worse than a defined threshold (Threshold1).
- A neighboring cell (NeighCell) signal quality becomes better than another defined threshold (Threshold2).
This dual condition ensures that handovers occur only when it is justified to switch from the current cell to a better alternative.
Note: You can test out Measurement Report Event A5 using the Measurement Events Simulator.
Why is Event A5 Important?
It optimizes handover decisions by:
- Reducing unnecessary handovers to weaker cells.
- Ensuring that the UE always connects to the most suitable cell for stable and efficient communication.
Measurement Event A5 conditions
Entering Event A5
The UE considers Event A5 to be triggered when both of the following conditions are met:
- Condition A5-1 (Entering condition 1): The serving cell signal strength (Mp + Hys) is worse than Thresh1.
Mp + Hys < Thresh1
- Condition A5-2 (Entering condition 2): The neighboring cell signal strength (Mn + Ofn + Ocn - Hys) is better than Thresh2.
Mn + Ofn + Ocn - Hys > Thresh2
Leaving Event A5
The UE considers Event A5 to no longer be valid when either of the following conditions are met:
- Condition A5-3 (Leaving condition 1): The serving cell signal strength (Mp – Hys) becomes better than Thresh1.
Mp – Hys > Thresh1
- Condition A5-4 (Leaving condition 2): The neighboring cell signal strength (Mn + Ofn + Ocn + Hys) becomes worse than Thresh2.
Mn + Ofn + Ocn + Hys < Thresh2
Key Variables:
- Mp: Measurement result of the serving cell (SpCell).
- Mn: Measurement result of the neighboring cell.
- Ofn: Measurement object-specific offset for the neighbor cell.
- Ocn: Cell-specific offset for the neighbor cell.
- Hys: Hysteresis parameter to prevent frequent toggling between states.
- Thresh1 & Thresh2: Threshold values for serving and neighboring cell quality, respectively.
Units of Measurement:
- RSRP: dBm.
- RSRQ & RS-SINR: dB.
- Offsets and hysteresis are expressed in dB.
eventA5 SEQUENCE {
a5-Threshold1 MeasTriggerQuantity,
a5-Threshold2 MeasTriggerQuantity,
reportOnLeave BOOLEAN,
hysteresis Hysteresis,
timeToTrigger TimeToTrigger,
useWhiteCellList BOOLEAN
}
MeasTriggerQuantity ::= CHOICE {
rsrp RSRP-Range,
rsrq RSRQ-Range,
sinr SINR-Range
}
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the hysteresis parameter Hys?
The hysteresis Hys prevents frequent, unnecessary handovers by adding a margin to the measurement thresholds. It ensures stability by requiring more significant changes in signal quality before triggering an event.
How are thresholds Thresh1 and Thresh2 configured?
- Thresh1: Represents the minimum acceptable quality for the serving cell.
- Thresh2: Represents the minimum required quality for a neighboring cell to be considered better.
These values are set in the network configuration based on deployment scenarios.
How does Event A5 prevent ping-pong handovers?
By using separate conditions for entering and leaving the event, with hysteresis applied, the UE avoids rapidly switching back and forth between cells.
References
- 3GPP TS 38.331: NR; Radio Resource Control (RRC); Protocol specification (Release 16)
- 3GPP TS 38.215: NR; Physical layer measurements
- 3GPP TS 38.300: NR; Overall description; Stage 2

WirelessBrew Team
Technical expert at WirelessBrew, specializing in 5G NR, LTE, and wireless system optimization. Committed to providing accurate, 3GPP-compliant engineering tools.
Up Next
More 5g nr Articles →