Mobility Robustness Optimization (MRO) in 5G NR
Mobility Robustness Optimization (MRO) in 5G NR
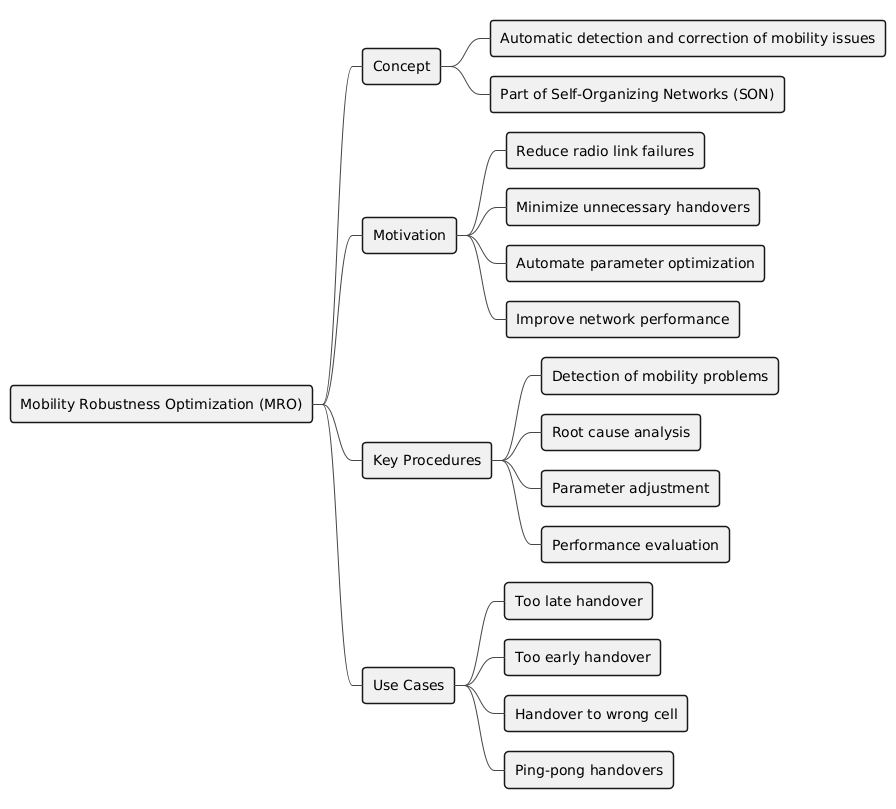
Mobility Robustness Optimization (MRO) is a critical feature in 5G NR designed to enhance handover performance and minimize mobility-related failures. Mobility management is essential for providing seamless user experience as UEs move across cell boundaries in the mobile network. MRO focuses on optimizing handover parameters and configurations to prevent Radio Link Failures (RLF), minimize Handover Failures (HOF), and reduce Ping-Pong effects in handover scenarios.
In 5G NR, the 3GPP has standardized various MRO techniques to achieve reliable mobility performance. These techniques are outlined in 3GPP Release 15 and subsequent releases, with specific focus on reducing mobility-related issues and enhancing network efficiency. MRO operates in both closed-loop and open-loop modes, using real-time network feedback and pre-configured parameters to optimize handover decisions. It continuously monitors network performance metrics and automatically adjusts the mobility parameters to improve handover success rates and reduce mobility-related failures.
Components of MRO in 5G NR
MRO consists of several components, each targeting specific mobility challenges:
- Handover Failure (HOF) Reduction
- Radio Link Failure (RLF) Prevention
- Ping-Pong Handover Mitigation
- Cell Reselection Optimization
Each of these components relies on optimized signaling, measurement reports, and mobility events to prevent unnecessary disruptions in the user experience.
Handover Failure (HOF) Reduction
Handover failure occurs when the UE cannot establish a connection with the target cell during a handover procedure. To address this, the network utilizes various handover parameter tuning methods defined in 3GPP TS 38.331. These include:
- Adjusting Time-to-Trigger (TTT): Delaying or expediting the handover process based on UE conditions.
- Configuring Events A3/A5: Early detection of deteriorating link quality prompts faster handover initiation.
- Dynamic Hysteresis: Modifying handover hysteresis to minimize false handovers and improve decision accuracy.
The MRO algorithms can trigger reconfiguration messages to UEs, dynamically adjusting handover parameters based on real-time network performance data.
Radio Link Failure (RLF) Prevention
RLF occurs when the signal quality between the UE and the serving cell deteriorates beyond recovery, leading to connection loss. The network can prevent RLF through enhanced monitoring of the RLF triggers specified in 3GPP TS 38.300. Measures include:
- Threshold-based RLF detection: The UE continuously monitors signal quality metrics such as RSRP and RSRQ. When these metrics fall below predefined thresholds, the network triggers corrective actions.
- Optimized Cell Individual Offset (CIO): The CIO parameter is tuned dynamically to optimize the handover margin between cells, preventing RLF due to poor coverage or interference.
These mechanisms allow the network to anticipate potential RLFs and execute proactive measures such as handover to a better cell or requesting the UE to perform a re-selection.
Ping-Pong Handover Mitigation
The Ping-Pong effect refers to the rapid back-and-forth handovers between two or more cells, which negatively impact the user experience. 3GPP TS 38.133 outlines techniques for mitigation:
- Hysteresis adjustment: Increasing handover hysteresis values to prevent unnecessary handovers.
- Mobility state detection: The network adjusts handover criteria based on the UE's reported mobility state (stationary, medium-speed, high-speed).
- TTT tuning: Increasing the Time-to-Trigger parameter allows the UE to remain connected to the serving cell longer.
Cell Reselection Optimization
For UEs in idle mode, cell reselection is the primary mobility procedure. 3GPP TS 38.331 specifies that the UE performs cell reselection based on ranking criteria (RSRP, RSRQ). MRO optimizes the reselection parameters to ensure the UE connects to the best available cell, especially in dense network environments.
MRO Process Overview

Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
To measure the effectiveness of MRO in 5G NR, several KPIs are monitored by the network:
- Handover Success Rate (HSR): The percentage of successful handovers. High HSR reflects effective MRO.
- Radio Link Failure Rate (RLF Rate): Number of RLFs per unit time/session. MRO aims to minimize this.
- Ping-Pong Rate: Number of unnecessary handovers between cells.
- Call Drop Rate (CDR): Number of dropped calls due to handover failures or RLFs.
Self-Optimization via SON
MRO is closely integrated with Self-Organizing Networks (SON) functions. SON algorithms continuously analyze performance data and apply corrective actions without human intervention. SON-based MRO ensures that handover thresholds, hysteresis, and CIO values are optimized in real-time.
MRO Process Flow
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of mobility events (handovers, HOFs, RLFs).
- Detection: Identifying potential problems like frequent HOFs or ping-ponging.
- Analysis: Analyzing root causes using signal quality measurements (RSRP/RSRQ) and signaling data.
- Optimization: Adjusting parameters (thresholds, TTT, hysteresis) based on analysis.
- Implementation: Applying new parameters to improve performance.
Key Parameters Optimized
- Time-to-Trigger (TTT): Duration signal quality must meet a threshold before handover triggering.
- Handover Margin (Hysteresis): Margin by which target signal must exceed source signal.
- Event A3: Trigger when target becomes better than source by an offset.
- Event A1/A2: Entry/exit thresholds for serving cell coverage.
MRO in 5G NR Context
In 5G NR, MRO is critical due to:
- Beam-based Mobility: Optimizing handovers between beams (beam-switching) in addition to cells.
- Dual Connectivity (DC): Optimizing handovers across LTE (anchor) and NR links.
- Ultra-Dense Networks: Managing frequent handovers in dense small cell deployments.
Benefits
- Reduced Handover Failures: Fewer dropped calls.
- Improved User Experience: Smoother transitions.
- Reduced Network Load: Less signaling overhead from failed/unnecessary handovers.
References
- 3GPP TS 38.300: Overall architecture and principles for NR.
- 3GPP TS 38.331: Radio Resource Control (RRC) protocol specification.
- 3GPP TS 38.413: NG-RAN application protocol for mobility.
- 3GPP TS 38.133: Requirements for RRM in mobility scenarios.
Further Reading
FAQ: Mobility Robustness Optimization (MRO)
What is MRO in 5G?
Mobility Robustness Optimization (MRO) is a feature of Self-Organizing Networks (SON) that automatically tunes handover parameters to ensure high mobility performance and minimize connection drops.
What are the main goals of MRO?
The primary goals are to reduce Handover Failures (HOF), prevent Radio Link Failures (RLF), and mitigate the Ping-Pong effect where a UE frequently switches between cells.
How does MRO detect a "Too Early" handover?
MRO identifies a "Too Early" handover if a Radio Link Failure occurs shortly after a successful handover, and the UE attempts to re-establish the connection in the source cell.
What parameters does MRO typically adjust?
MRO optimizes parameters such as Time-to-Trigger (TTT), handover hysteresis (margin), and Cell Individual Offsets (CIO).
WirelessBrew Team
Technical expert at WirelessBrew, specializing in 5G NR, LTE, and wireless system optimization. Committed to providing accurate, 3GPP-compliant engineering tools.
Up Next
More 5g nr Articles →